Top 10 Tips for Successful Prototype Injection Molding You Need to Know
In the realm of product development, prototype injection molding has emerged as a pivotal technique for bringing ideas to life and refining designs before full-scale production. This method offers rapid turnaround times and cost-effective solutions, making it an ideal choice for startups and established companies alike. However, successful prototype injection molding requires a solid understanding of both the technical and practical aspects involved in the process.
This article presents the top 10 tips that are essential for achieving optimal results in prototype injection molding. From material selection to mold design and the importance of iterative testing, these insights will provide a comprehensive foundation for anyone looking to navigate the complexities of the molding process. By adhering to these tips, designers and engineers can enhance the efficiency and quality of their prototypes, ultimately leading to more successful product launches.

Understanding the Basics of Prototype Injection Molding
Prototype injection molding is a critical process in product development, allowing designers and engineers to create tangible models of their concepts. Understanding the basic principles behind this manufacturing technique is essential for anyone looking to bring their ideas to life. The process begins with the design of a mold, which is the negative form into which molten plastic is injected. This mold is typically crafted from materials such as steel or aluminum, which can withstand high temperatures and pressures.
Once the mold is prepared, the next step involves heating plastic pellets until they become molten. The molten plastic is then injected into the mold cavity under high pressure, allowing it to fill the intricate details and contours of the design. After allowing the material to cool and solidify, the mold is opened to reveal the finished prototype. This technique enables rapid iterations, as multiple prototypes can be produced quickly, allowing for testing and modifications before moving to full-scale production. Understanding these fundamentals not only helps in optimizing the design but also in streamlining the production process for successful results.
Top 10 Tips for Successful Prototype Injection Molding
Essential Materials for Effective Prototype Production
When it comes to effective prototype production in injection molding, selecting the right materials is crucial. The choice of material not only influences the overall design and functionality of the prototype but also affects the cost and lead time. Common materials used in prototype injection molding include thermoplastics such as ABS and polycarbonate, known for their ease of molding and durability. These materials provide a good balance between performance and cost, making them ideal for initial prototypes that require testing and validation.
One of the important tips for successful prototype injection molding is to ensure that the material choice aligns with the intended use of the prototype. For example, if the prototype needs to endure higher temperatures, materials with higher thermal resistance should be selected. Additionally, incorporating additives can enhance specific properties like impact resistance or flexibility, tailored to the prototype's requirements.
Another tip focuses on the importance of thorough material testing before proceeding to full-scale production. This step allows designers to identify any potential issues or limitations that the selected materials may have in real-world applications. Through iterative testing and evaluation, designers can optimize their prototypes, ensuring that the final product meets performance standards and user expectations.
Design Considerations for Successful Injection Mold Prototypes
When designing injection mold prototypes, the consideration of material selection and geometrical complexities plays a crucial role in achieving successful outcomes. Different materials exhibit unique behaviors under heat and pressure, which can significantly affect the quality and integrity of the final product. For instance, materials like thermoplastics provide better flow characteristics, allowing for intricate designs and tighter tolerances. It's essential to match the material properties with the prototype's functional requirements to ensure that the final mold can withstand the intended application.
Another vital aspect to consider is the design of the mold itself, which should incorporate features that facilitate manufacturing and assembly. Draft angles, fillets, and ribbing are essential design elements that help in the easy ejection of parts and enhance the strength of the prototype. A well-thought-out gate design can also minimize material waste and control the flow into the cavity, ensuring consistent part quality. By prioritizing these design considerations, you can optimize the injection molding process and improve the efficiency of prototype development.
Top 10 Tips for Successful Prototype Injection Molding You Need to Know
| Tip Number | Tip | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Material Selection | Choose the right plastic material for your prototype to ensure it meets performance requirements. |
| 2 | Design for Manufacturability | Ensure your design can be easily produced by considering wall thickness, part geometry, and features. |
| 3 | Prototype Orientation | Orient the prototype in the mold to minimize defects and improve material flow. |
| 4 | Cooling System Design | Design an efficient cooling system to reduce cycle times and prevent warping. |
| 5 | Use Closing Features | Incorporate closing features in the design to improve rigidity and reduce sink marks. |
| 6 | Specify Tolerances | Provide precise tolerances in your CAD models to ensure proper fit and function of components. |
| 7 | Test Early and Often | Conduct thorough testing on prototypes to identify issues early in the development process. |
| 8 | Consider Volume Production | Think ahead about your production volume to select appropriate materials and processes. |
| 9 | Engage Experts | Work with molding professionals for advice on complex designs and best practices. |
| 10 | Iterate Based on Feedback | Use feedback from tests and users to improve the design before final production. |
Key Processes Involved in Prototype Injection Molding
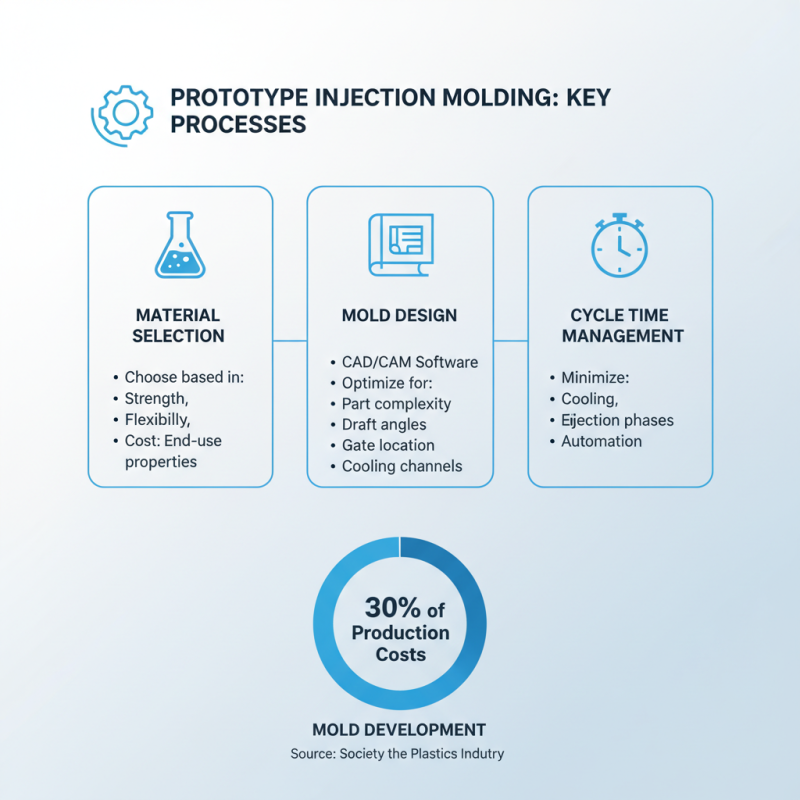
Prototype injection molding is an essential process in product development, enabling designers and engineers to create reliable prototypes for testing and feedback. The key processes involved in this technique include material selection, mold design, and cycle time management. According to a report by the Society of the Plastics Industry, approximately 30% of the total production costs can be attributed to mold development, highlighting the importance of investing time and resources into creating an efficient mold design.
Material selection plays a crucial role as well, with over 70% of prototyping projects utilizing thermoplastics due to their versatility and ease of processing. Different types of thermoplastics offer various properties, allowing for customization based on the requirements of the prototype, such as flexibility, strength, or heat resistance. Furthermore, understanding the cycle time is imperative for project timelines. Typical cycle times in prototype injection molding can range from 30 seconds to several minutes, depending on part design and complexity, necessitating precise planning to meet development needs without undue delays. Effective management of these key processes ensures that prototype injection molding is not only successful but also optimized for cost and efficiency.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them in Prototyping
When embarking on a prototype injection molding project, awareness of common challenges can significantly enhance the likelihood of success. One prevalent challenge is achieving dimensional accuracy, which has been reported to affect nearly 70% of prototypes created through traditional methods (Source: AMI Consultants). Fluctuations in temperature, variances in material properties, and tooling issues can lead to discrepancies from the intended design. To mitigate these issues, it is crucial to rigorously control the molding process parameters. Conducting pre-molding simulations using software can predict potential problems, allowing engineers to fine-tune designs before metal is cast.
Another frequent obstacle in prototyping is material selection, where decisions can inadvertently impact both the look and functionality of the final product. A survey conducted by the Plastics Industry Association revealed that 48% of companies underestimate the importance of choosing the right resin for their prototypes. This misstep can result in prototypes that are not only structurally unsound but also fail to meet aesthetic expectations. To address this, companies should invest time in researching various materials' properties and engaging with suppliers to understand the latest advancements in resin technologies. Implementing a phased approach to testing different materials can provide valuable insights into their performance, ultimately streamlining the prototyping process and enhancing end results.
Related Posts
-

Understanding the Benefits of Prototype Injection Molding for Fast Product Development
-

The Future of Injection Tooling in Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
-

Understanding the Injection Molding Process for Sustainable Product Development
-

2025 Top 10 Innovations Revolutionizing the Injection Molding Process
-

Exploring the Future of Injection Molding Materials: Innovations and Trends Shaping the Industry
-

Understanding Plastic Injection Tooling: The Key to Optimizing Manufacturing Efficiency in 2023
